What is new in Windows 11 ?
If you need Help!
- You can report an incident / submit a request.
- You can also reach the Service Desk by phone at 77777 or by e-mail at service-desk@cern.ch.
- More info about Windows 11 (external link).
Windows 11 is the latest version of Windows. It was launched by Microsoft in final version on September 5, 2021.
At CERN, Windows 11 is available since November 8, 2021. It can be installed from the PXE network boot menu DIANE if your machine is eligible.
An In-Place upgrade CMF package is also available in CMF for machines running Windows 10 > b2004 which are eligible for Windows 11. So, if you see the CMF package called MS Windows 11 22H2 in-place upgrade from any build in CMF Add/Remove CMF package, it means you can upgrade.
The newest version of Microsoft Windows 11 requires higher system configurations to run like Intel Core i Series 8th generation, AMD Zen+ series, and later. It requires also TPM 2.0 as well as secureboot to be enabled on your machine.
PC Health Check
How to use the PC Health Check app ?
- This upgrade to Windws 11 only applies to PCs that pass testing of Microsoft's PC Health Check app (external link), including the TPM 2.0 requirement.
Is your device eligible to upgrade windows 11 ?
Follow the next steps:
- Download the PC Health Check app found on the link provided above.
- Run the downloaded file and follow the onscreen instructions to start the installation process.
- When installation has finished, run the application and you should see the "PC health at a glance" screen.
- Under the Introducing Windows 11 section, click the Check now button.
- When completed you will see one of two messages, either "This PC can run Windows 11" or "This PC can't run Windows 11".
If you are running a device centrally managed at CERN, you will receive the following warning message.
Your organisation manages updates on this PC
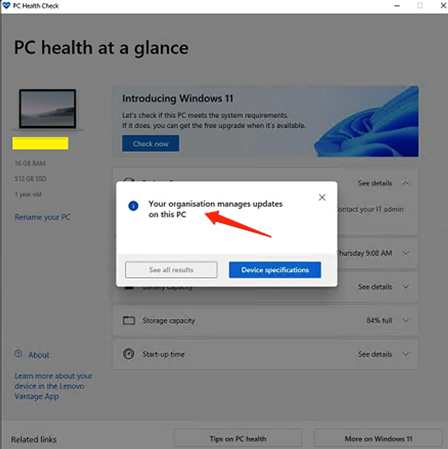
To work around this limitation, please read the following steps or simply check if you see the CMF package called "MS Windows 11 22H2 in-place upgrade from any build" in CMF "Add/Remove CMF package", it means you can upgrade.
Another way to ckeck the eligibility of your current device to upgrade Windows 11
- Launch PowerShell ISE as administrator
- In Search, type ISE, right-click Windows PowerShell ISE, and then click Run as administrator.
-
Paste in this script to both download (1) and run the script (2)
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force Invoke-WebRequest -Uri 'https://aka.ms/HWReadinessScript' -OutFile .\Windows11HWReadiness.ps1 . .\Windows11HWReadiness.ps1 -
After running, you should see a small table. Here is what it looks like. (see the image below)
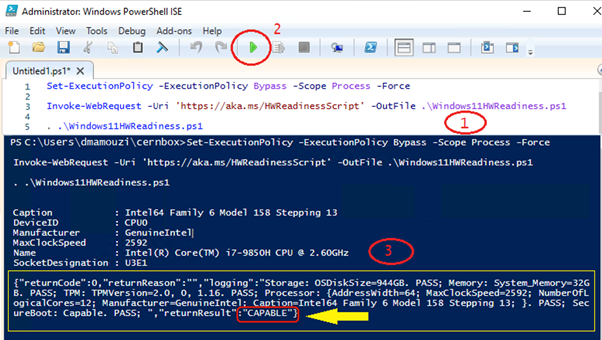
- Then, look for the value of “returnResult” (3). If it says CAPABLE, your device is eligible to upgrade.
Here is a scenario where it is not possible to upgrade:
{"returnCode":1,"returnReason":"Storage, TPM, SecureBoot, ","logging":"Storage: OSDiskSize=40GB. FAIL; Memory: System_Memory=7GB. PASS; TP M: TPMVersion=False. FAIL; Processor: {AddressWidth=64; MaxClockSpeed=2095; NumberOfLogicalCores=2; Manufacturer=GenuineIntel; Caption=Int el64 Family 6 Model 85 Stepping 4; }. PASS; SecureBoot: Not capable. FAIL; ","returnResult":"NOT CAPABLE"}
Understanding the Hardware Readiness script output
The Hardware Readiness script is meant to determine if a device meets the minimum system requirements for Windows 11, and in the case that not all requirements are met, it will highlight which hardware checks failed. Results are returned with four key/value pairs:
- returnCode: an integer value that represents whether the device meets the minimum system requirements for Windows 11. Possible results include:
| returnCode | Definition |
|---|---|
| -2 | FAILED TO RUN – the script encountered an error |
| -1 | UNDETERMINED – one or more of the hardware requirement checks failed to execute properly |
| 0 | CAPABLE – the device meets all assessed Windows 11 hardware requirements |
| 1 | NOT CAPABLE – the device does not meet one or more of the assessed Windows 11 hardware requirements |
-
returnReason: a string value that provides a comma-separated list of the Windows 11 hardware requirements that are not met on the device. Possible results include: Storage, Memory, TPM, Processor and SecureBoot.
- For instance, if the script is run on a device that meets all hardware requirements except the Storage requirement, returnReason would equal “Storage.” In the case that all hardware requirements are met, returnReason will be NULL.
-
logging: a string value that provides verbose logging of the determined values for all hardware checks performed on the device.
- returnResult: a string value that is a human-readable representation of returnCode. Possible results include: CAPABLE, NOT CAPABLE, UNDETERMINED, and FAILED TO RUN.
Performance improvements
Windows 11 has major performance improvements from Windows 10. It brings good optimization of the system apps in the background and ensures great battery life at a high-performance time.
The design and experience of Windows 11 have been simplified to promote productivity and inspire creativity. The graphical theme of the OS is much lighter than Windows 10. The dark theme is still available.
Start menu and Taskbar
Visually, the Start menu and the taskbar are the most significant differences between Windows 10 and Windows 11. In Windows 11, the taskbar and the Start menu are placed in the centre of the screen (see image above). Windows 11 looks a bit like macOS and ChromeOS. However, it is possible to move it to the left as needed.
- The Start menu
It's a little more simplistic than in Windows 10. Visually, we only see a static list of apps, followed by the most used documents at the bottom. One can open the app list, scroll through the list, and pin apps as one chooses. It may sound familiar, but Windows 11 no longer supports Live Tiles. Start menu icons are now transparent with rounded corners. They are further apart from each other. The user will be able to pin them according to their preferences. The interface seems to mimic that of MacOS. Under the pinned applications, the menu shows the last files used within the Microsoft 365 suite, regardless of the user's device where they were created (Windows, iOS or Android). As for the Task Manager and the old Control Panel, they are still present.
- The Taskbar
How to use the Taskbar in Windows 11 ? (external link)
There are some big changes. Microsoft reduced the search box to an icon and removed Cortana functions. If you want Cortana, you will need to download it. The search function also moves to the centre of the screen, with a floating design and tabbed layout like Windows 10. Windows Timeline is gone. This feature available on Windows 10 has disappeared in favour of the synchronization capacity of Microsoft Edge. The vacant space is replaced by virtual offices.
It will no longer be possible to pin the taskbar to the right or left of the screen. The taskbar will remain only at the bottom of the screen.
Many of these changes are merely visual. Windows 11 and Windows 10 share the same features, and it is just the way things look that is different.
Improved multitasking and virtual desktop support
How to snap your windows? (external link)
On the productivity side, Windows 11 improves multitasking. Thus, it allows via the Snap Layouts function, to display simultaneously on the screen up to 3 application windows side by side by choosing the desired layout. As for the Snap Groups device, it allows you to return to an arrangement already used through the taskbar.

How to create multiple virtual office ? (external link)
In one click, the user can save the layout in question in a virtual office to pass it on from his workstation to his laptop or tablet. As on Windows 10, he will be able to create as many virtual desktops as necessary, for work and for home.
Information widgets
Windows 11 also introduces information widgets: weather, stock market, news... Nestled in a retractable side panel, they can be arranged according to the user's interest, but also refer to applications such as Calendar or Task Manager. Widgets are available on the Taskbar.
Redesigned Microsoft Store and Android Apps integration.
With Windows 11, Microsoft Store has been redesigned. And not just in terms of GUI. It now includes both applications, but also games or film offers. Microsoft Store integrates older generation Windows software (Win32) in .msi or .exe format for the first time. There are now applications such as Adobe Acrobat Reader, Zoom, LibreOffice, Discord, VLC, TeamViewer ... and more.
The OS introduces support for Android apps for the first time. It allows users to now run Android applications on their Windows computers Their download goes through the Amazon app store which is integrated into the Microsoft Store. These applications take advantage of the entire Windows environment, from the notification center to the Start menu through multitasking. This allows users to run the same applications that they use on their phone now on their PC, for effective synchronization techniques.
Why installing Windows 11 ?
Windows 11 introduces a new ergonomics. Still at the bottom of the OS interface, the Start menu and the taskbar move from the right of the screen to the center. It is possible to return to the Windows 10 interface through the settings.
Beyond this cosmetic change, the main evolution of Windows 11 compared to Windows 10 lies in its security, and in particular the support for TPM 2.0 encryption technology. A security layer leans directly against the processor of the terminal. This hardware encryption is by definition harder to crack than software encryption.
Hardware requirements
Windows 11 requirements (external link)
To install or upgrade to Windows 11, devices must meet a minimum hardware requirements. Your device must be running Windows 10, version 2004 or later, to upgrade. Free updates are available through Windows Update in Settings | Update and Security.
| Element | Minimum requirement |
|---|---|
| Processor | 1 GHz or faster with two or more cores on a compatible 64-bit processor or system on a chip (SoC). |
| RAM | 4 gigabytes (GB) or greater. |
| Storage | 64 GB or greater available storage is required to install Windows 11. |
| Additional storage space might be required to download updates and enable specific features. | |
| Graphics card | Compatible with DirectX 12 or later, with a WDDM 2.0 driver. |
| System firmware | UEFI, Secure Boot capable. |
| TPM | Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0 |
| Display | High definition (720p) display, 9" or greater monitor, 8 bits per color channel. |
| Internet connection | Internet connectivity is necessary to perform updates, and to download and use some features. |
Main differences between Windows 11 and Windows 10
| Windows 11 | Windows 10 |
|---|---|
| Based on macOS functionality. | Based on Android functionality. |
| Windows can now install Android, iOS, and Windows apps. | Windows can install only Windows apps. |
| Only runs on devices with TPM 2.0 | Only runs on devices with TPM 1.2 or above. |
| Only runs on devices with a minimum of 4GB RAM and 64GB storage. | Only runs on devices with a minimum of 2GB RAM and 32GB storage. |
| Only runs on devices with Intel Core i Series 8th generation, AMD Zen+ series processors or higher. | Only runs on devices with Intel Core i Series 4th generation series processors or higher. |
| Start menu in the centre of the screen but it can be changed. | The Start menu to the left of the screen. |
| Microsoft Teams is integrated within the OS and there is no separate app. | Microsoft Teams is a separate part ofTthe OS and need to be installed separately. |
| Windows 11 features faster unlock timing and more efficient performance. | Windows 10 introduced these features the first time, so they were not as effective as Windows 11. |